Exploring Withdrawal Rates That Can Pay You A Bonus
Will you have enough retirement income with a 4% safe withdrawal rate? What if the markets perform poorly, do you adjust your withdrawals? And if the markets perform well, do you withdraw more money? The good news is that there are flexible withdrawal strategies to help your money last longer.
The safe withdrawal rate is the maximum amount of money that you can withdraw from your retirement savings every year without running out of money. The withdrawal rate is calculated by taking 4% of your starting balance as income while allowing you to increase your income by the inflation rate each year.
The 4% rule as it’s now dubbed, was designed to be the worst-case scenario given market corrections over a 35-year period. It has since become the default withdrawal rate for those in retirement who want to know how much they can safely withdraw for income without outliving their savings.
Over the years, there has been much debate as to whether the 4% withdrawal rate is too aggressive, especially in the early years of retirement. Others argue the rate is too conservative. Also, interest rates are far lower today than when the safe withdrawal rate was introduced in 1994.
Whether the markets perform well or perform poorly, there are flexible variations of the 4% rule, designed to help your money last longer while also allowing you to increase your income from time to time when the markets perform well. In this article, we’ll analyze a couple of those strategies.
FLEXIBLE SAFE WITHDRAWAL RATE STRATEGY:
Safe Withdrawal Rate With A Balance Trigger
The 4% rule calculates your yearly income amount so that it provides enough income in case of market corrections in retirement, but it doesn’t necessarily mean that you can’t take more money out if the market does well. In the upcoming examples, Social Security income is not factored in for ease of discussion. We’ll address Social Security after we review the strategies.
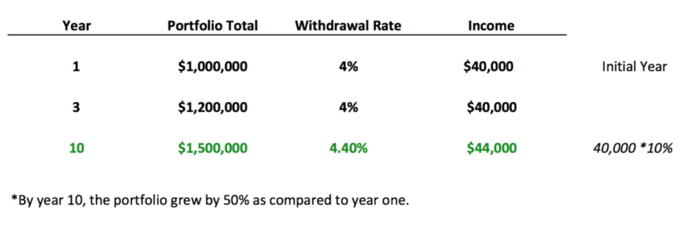
Below is a variation of the 4% rule, except it allows you to increase your income withdrawal rate only if your retirement portfolio has grown by 50% from the starting balance.
- In the table below, we can see that in year one, Mary has $1,000,000 saved for retirement. Her withdrawal amount is $40,000 at a 4% safe withdrawal rate.
- Each year afterward, Mary can withdraw $40,000 plus any adjustments for inflation increases. Please note, in this example, we’ll assume inflation is zero.
- By year ten, Mary’s retirement balance has grown to $1,500,000 due to gains in the financial markets.
- Mary can increase her withdrawal amount by 10% boosting her income to $44,000 in year ten (10% * $40,000).
- Mary’s withdrawal rate is now 4.4% (10% added to the 4% original safe withdrawal rate equaling .4% for a total of 4.4%).
 Please note, the increases in the withdrawal rate are calculated off Mary’s starting balance of $1,000,000 not the new higher balance of $1.5mm.
Please note, the increases in the withdrawal rate are calculated off Mary’s starting balance of $1,000,000 not the new higher balance of $1.5mm.
Benefits And Key Factors:
This strategy allows Mary’s savings to grow for a few years before she can withdraw any additional income. The balance contingency helps preserve Mary’s savings while allowing her the option to increase her income when her portfolio has grown by 50%. In short, Mary gets to enjoy her retirement as her portfolio grows.
An income floor of $40,000 is established whereby Mary will never take out a lower income than year one’s initial withdrawal amount.
Flexibility is allowed provided you don’t overspend. The above example can be modified. For example, instead of 50%, you might increase your withdrawal rate if the balance grew by 30%. Also, increases in income can be limited to no more than two years, for example, so not to overdo it. However, before making any decision, please consult your financial planner to ensure you don’t increase your income by too much and risk running out of money in later years.
FLEXIBLE SAFE WITHDRAWAL RATE STRATEGY:
Base Pay Plus A Bonus
In our next strategy, you start off your retirement with a safe withdrawal rate that pays your need expenses, such as electricity, food, etc. This is your base pay or salary.
You can increase your withdrawal rate only if your portfolio performs well. This is your bonus pay for your want expenses. Let’s look at an example.
Base-Pay Plus A Bonus Strategy Example:
Joe has $1,200,000 saved for retirement and has opted to withdraw 3% per year of his starting balance. This is his base-salary. However, if his portfolio grows by 10% or more for two consecutive years, Joe’s withdrawal rate increases to 4% as a bonus.
- Joe’s base salary in retirement will be $36,000 not including Social Security benefits.
- From the table we see, Joe earns $36,000 in his first few years of retirement.
- In years 4 and 5, Joe’s portfolio grows by more than 10%.
- In year 6, Joe’s bonus kicks in, and he withdraws $48,000 as income.
- In year 7, Joe withdraws 4% again as his portfolio continued to grow by over 10%.